Customer pain points are the problems that your customers are facing. They can be anything from technical issues to logistical challenges to simply not getting what they need from your product or service.
These pain points for customers manifest in various ways – from confusion during the buying process to difficulties with product features or unsatisfactory support experiences.
Reality check: 32% of customers would stop doing business with a brand they loved after just one bad experience.
By identifying and addressing customer’s pain points early, you can reduce customer churn by up to 67%. So, let’s explore how to identify, analyze, and resolve the issues that matter most to your customers.
Reduce churn by continuously engaging customers with WPLoyalty’s loyalty programs and retain more loyal customers.
What Are Customer Pain Points?
Customer pain points are the issues or problems that customers face when using your product or service. It occurs at various stages of the customer journey – from initial research and product evaluation to post-purchase support.
Statista’s 2024 survey found that extra costs and fees were the top pain points for 48% of shoppers which led to cart abandonment. In another survey that same year, global consumers identified extra costs at checkout (30%) and limited payment methods (17%) as main reasons for cart abandonment globally.
Here’s a breakdown of common customer pain points typically emerge:
| Industry | Primary Pain Points | Impact Rate (%) |
| E-commerce | Unexpected shipping costs, high return fees, complex checkout process, account creation requirements, difficult order tracking, slow return processing. | 84% |
| Healthcare | Unexpected charges, insurance complexities, appointment scheduling, paperwork, follow-up care, communication gaps. | 81% |
| Banking | Hidden fees, minimum balance requirements, account opening, loan applications, response time, issue resolution. | 80% |
| Software | Expensive upgrades, complex pricing tiers, bugs, feature limitations, poor UI/UX, limited support hours, automated responses. | 77% |
| Insurance | Premium increases, unclear coverage costs, claims processing, documentation. | 81% |
| Media | Content accessibility/quality, loading speed, streaming issues. | 78% |
Types of Customer Journey Pain Points
While customer pain points can manifest in various ways, they typically fall into four main categories:
Financial Pain Points
These are customer experience pain points related to the cost of products or services, including pricing, fees, and billing. Examples include:
- High prices or unexpected costs
- Unclear or hidden fees
- Complicated payment processes
- Difficulties with refunds or returns
Product Pain Points
These are problems with the quality, features, or functionality of a company’s products or services. Examples include:
- Defects, bugs, or reliability issues
- Missing key features or capabilities
- Confusing or difficult-to-use interfaces
- Compatibility problems across devices/platforms
Process Pain Points
These are challenges customers face navigating a company’s procedures, policies, and customer journey. Examples include:
- Complex account setup or onboarding
- Cumbersome purchase or checkout flows
- Inefficient customer support processes
- Difficulties accessing information or self-service options
Support Pain Points
These are issues with the quality and responsiveness of a company’s customer service. Examples include:
- Long wait times for assistance
- Unhelpful or impersonal support interactions
- Inability to reach a live agent when needed
- Lack of communication or status updates
How to Identify Customer Pain Points?
To identify customer pain points, you can:
1. Conduct customer surveys and ask for feedbacks
Surveys allow you to ask targeted questions that directly address possible frustrations, unlike general analytics, which only show outcomes without context.
Use sentiment analysis tools to guess customer emotions in feedback. Also, mix quantitative surveys (e.g., Net Promoter Score, Customer Effort Score) and qualitative feedback (e.g., open-ended questions, post-interaction surveys) to gather valuable data.
Examples of questions to ask:
- “What difficulties have you encountered when using our product?”
- “What changes would make our service more valuable to you?”
- “How could our processes be more convenient or user-friendly?”
Sales reps are on the frontline with potential customers who voice their concerns and reasons for hesitating.
This access makes them uniquely capable of identifying not just pain points but recurring objections, which is insight that data alone can’t reveal.
For example, you could ask:
- “What are the most common hesitations from prospects?”
- “What features or solutions do customers frequently ask about?”
- “Are there common misunderstandings during the buying process?”
2. Use Social Listening
Customers are often more honest on social media, forums, and review sites where they share frustrations openly.
Social listening captures this feedback in real-time, helping you stay proactive rather than waiting for formal feedback to trickle in.
For example, if users frequently post about “frustration with setup” or “lack of support,” it can signal a process or service gap worth addressing.
3. Follow-up with customer complaints
Complaints highlight the issues that impact customers enough to take action.
Addressing these proactively turns negatives into positives, showing that you care about improvement, which builds loyalty.
After a complaint is resolved, consider asking the customer follow-up questions like:
- “How could we improve our approach to this issue?”
- “What would make it easier to get the help you need?”
- “How can we prevent this from happening again?”
4. Use Customer Journey Mapping
Create a detailed visual representation of your customers’ end-to-end journey. Identify pain points at each stage, from product discovery to post-purchase support.
Unlike singular feedback, it shows a pattern of challenges across stages, letting you address root causes rather than symptoms.
For example, you might find that most customers drop off at the account setup stage or experience delays in post-purchase support. By visualizing these pain points, you can create a strategy to simplify complex stages or speed up support processes.
5. Conduct Customer Support Interactions
Support teams handle recurring problems directly, so they have unparalleled insight into frequent frustrations.
Each support call or ticket represents a potential improvement opportunity that analytics might overlook.
Consider creating a brief survey after support interactions to ask questions like:
- “Was your issue resolved to your satisfaction?”
- “What could we improve about our support process?”
- “Is there anything we could have done to prevent this issue?”
Common Customer Pain Points (with Examples)
B2B Customer Pain Points
- Complex Onboarding Processes
- Example: A B2B SaaS company with intricate software might face complaints from new clients struggling to set up and configure the platform without guidance.
- Solution: Streamline onboarding with step-by-step guides, video tutorials, and dedicated support for acquiring new customers.
- Hidden or Unpredictable Costs
- Example: Companies in logistics or cloud computing sometimes introduce extra fees for overages, leaving clients frustrated.
- Solution: Offer transparent pricing and upfront information on additional fees. Consider pricing calculators or a fixed pricing model.
- Limited Customization
- Example: Clients using marketing automation tools may require customization for their industry, and a lack of this flexibility creates friction.
- Solution: Build modular features, allowing businesses to customize their setup without additional costs or development.
- Lengthy Response Times for Support
- Example: When high-value B2B clients experience critical issues, slow responses impact their operations.
- Solution: Provide priority support tiers, with dedicated agents and shorter SLAs (Service Level Agreements) to address urgent client needs swiftly.
B2C Customer Pain Points
- Unexpected Checkout Costs
- Example: In e-commerce, unexpected shipping fees at checkout lead to high cart abandonment rates.
- Solution: Display shipping costs early in the purchase flow and consider offering free shipping thresholds.
- Difficult Return Processes
- Example: Retail brands often lose customers who find it too challenging or costly to return products.
- Solution: Simplify return policies and consider prepaid return labels to make the process hassle-free for customers.
- Poor User Interface (UI) or User Experience (UX)
- Example: A streaming service with a cluttered UI makes it hard for users to find content, reducing customer acquisition and retention.
- Solution: Prioritize user-friendly design and test interfaces with real users to identify and resolve pain points.
- Inconsistent Customer Support
- Example: Customers get frustrated when support responses vary in quality across different channels.
- Solution: Standardize training and establish clear support protocols to ensure consistent, quality interactions across channels.
These examples give a practical view of specific pain points in B2B and B2C contexts.
How to Solve Customer Pain Points?
To solve customer pain points:
1. Provide Fast, Accessible Support
- Use live chat and chatbots for immediate assistance.
- Create a self-service help center with FAQs, guides, and troubleshooting steps.
- For urgent issues, consider 24/7 support or priority service during peak times.
- Goal: Reduce wait times and provide prompt solutions through direct support channels.
2. Be Transparent with Pricing
- Display all fees clearly from the start to avoid surprises at checkout.
- For services with multiple pricing options, offer a clear breakdown of each pricing tier.
- Use cost calculators if there are variable fees to show upfront costs.
- Goal: Build trust by eliminating hidden fees, which are a major pain point.
3. Offer Consistent Experiences Across Channels
- Ensure that customers have a smooth, unified experience whether they’re using your website, app, phone support, or social media.
- Integrate customer data to allow for seamless support transitions between channels.
- Goal: Avoid mixed messages and ensure a smooth, cohesive experience regardless of where customers seek support.
4. Simplify the Customer Journey
- Use guest checkout options in e-commerce to avoid mandatory account creation.
- Minimize form fields and unnecessary steps during checkout or onboarding.
- Goal: Make purchases and sign-ups faster and easier, reducing abandonment rates.
5. Improve Product Quality
- Regularly test and update products to resolve known issues.
- Use customer feedback and analytics to identify recurring issues and address them quickly.
- Goal: Reduce customer complaints related to product quality.
6. Keep Staff Knowledge Up-to-Date
- Provide regular training on product knowledge, policies, and customer interaction skills.
- Encourage continuous learning to keep agents informed on new features and updates.
- Goal: Ensure accurate information and quicker problem resolution for customers.
7. Act on Customer Feedback for Continuous Improvement
- Send follow-up surveys after support interactions to understand pain points.
- Analyze trends in complaints to identify common issues and guide improvements.
- Goal: Use feedback to make ongoing adjustments and resolve pain points proactively
4 Major Industry-Specific Customer Pain Points with Solutions
- Customer pain points in retail
- Customer pain points in banking
- Customer pain points in healthcare
- Customer pain points in e-commerce
| S.no | Industry | Major Pain Points | Solutions |
| 1. | Retail | Inventory shortages and stockouts | Use real-time inventory tracking and alerts to restock quickly |
| Long checkout times | Implement mobile POS systems, self-checkout, and express lines | ||
| Inconsistent product availability across channels | Unify inventory systems to support ‘buy online, pick up in-store’ options | ||
| 2. | Banking | Hidden fees and complex pricing | Provide transparent pricing with clear fee breakdowns on statements and mobile apps |
| Limited access to customer support | Offer 24/7 support with chatbots and a comprehensive self-service knowledge base | ||
| Slow and lengthy application processes | Simplify applications with digital signatures and online account setups | ||
| 3. | Healthcare | Complicated billing and insurance issues | Offer clear billing statements, cost estimators, and trained billing support |
| Long waiting times for appointments | Provide online scheduling, telemedicine options, and virtual check-ins | ||
| Communication gaps between providers and patients | Use patient portals for record access and direct communication channels | ||
| 4. | E-Commerce | Unexpected shipping costs and long delivery times | Display shipping costs early and provide accurate delivery timelines |
| Complex return processes | Streamline return processes with prepaid labels and simplified instructions | ||
| Lack of payment options | Offer diverse payment methods like digital wallets and buy-now-pay-later options |
Customer Journey Map with Pain Point Intensity
- Awareness (discovering your brand)
- Consideration (evaluating products/services)
- Purchase (buying process)
- Onboarding (starting with the product)
- Usage (regular engagement)
- Support (when they need help)
- Loyalty/Advocacy (repeat usage or referral)
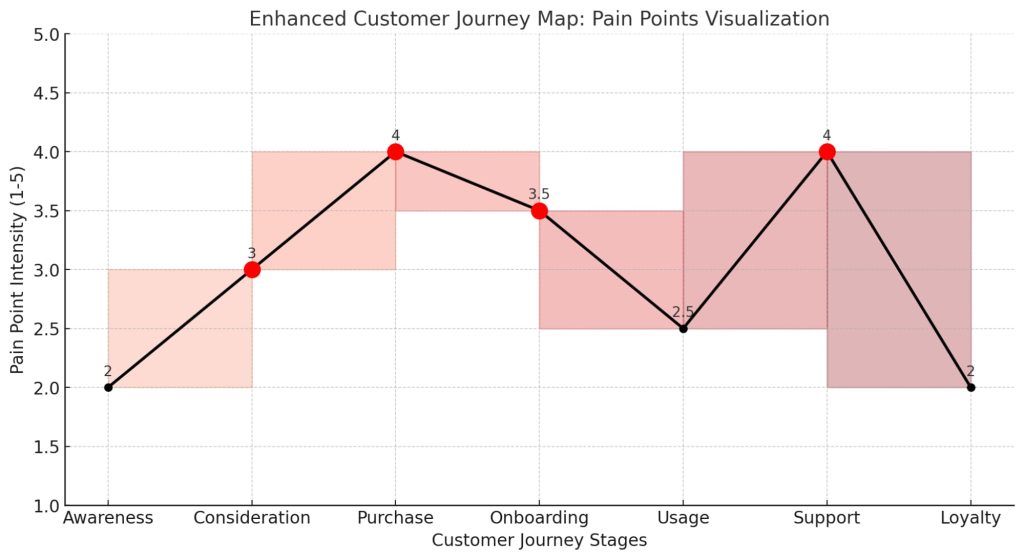
Here’s the customer journey map, showing pain point intensity across each stage from Awareness to Loyalty. The peaks indicate stages where pain points are more intense, helping to visualize areas that require focused improvements.
High-intensity stages (above 3) are marked in red, making it easy to spot critical areas where customer pain intensifies.
Get started with WPLoyalty’s prebuilt loyalty programs and reward customers with discounts to tackle customer drop-off today.
Final Words
Every customer pain point you resolve brings you closer to building loyalty and trust. When you take the time to map out where customers struggle and implement clear, practical solutions, you’re giving them a reason to keep choosing you.
Other helpful blogs:
- Loyalty Program Management: 10 Best Practices + Softwares
- Tiered Loyalty Programs: A Complete Guide
- How to Reward Loyal Customers: 10 Best Ways
- How to Build a Reward Point System for Customers (+Tips)
- 50 Best Referral Program Examples That Actually Work
Frequently Asked Questions
Unexpected costs at checkout, complicated return policies, and lack of payment options are common pain points in online shopping that frustrate customers.
Use surveys, customer feedback, and social listening to identify pain points. Engage with support teams and analyze complaints to uncover recurring challenges.
Identify pain points through data collection, prioritize based on impact, implement targeted solutions, and continually monitor for improvement.
Listen actively, empathize, and acknowledge their frustration. Offer solutions, and follow up to ensure satisfaction, turning negative experiences into positive ones.
Responsiveness, empathy, and knowledge are essential. Good customer service means understanding customer needs, providing timely solutions, and ensuring a smooth, helpful experience.