When it comes to customer strategy examples, the best ones all share a common goal: making customers feel valued.
Today, while 89% of businesses compete on customer experience, only a small fraction truly succeed at it. This gap leads to missed sales and weaker loyalty.
But here’s the good news: successful customer strategies don’t need big budgets or complex systems. They simply require understanding what customers want and adapting to meet those needs.
In this blog, we’ll explore:
- What customer strategy really means
- 8 proven customer strategy examples
- Practical steps to implement these strategies in your own business
- How Customer Strategy Varies by Industry
What is Customer Strategy?
A customer strategy is a carefully designed plan that companies use to make sure their interactions with customers are positive and valuable. Instead of only focusing on selling products or services, a customer strategy centers around the entire experience a customer has with a company.
Customer-centric strategy takes into account what customers need, their preferences, and how they feel about their experience with the company.
Key components of a successful customer strategy:
- Customer Engagement: Keeping customers actively involved and interested.
- Customer Retention: Encouraging customers to return instead of switching to competitors.
- Customer Experience: Ensuring every interaction is smooth and positive.
- Customer Feedback: Listening to what customers have to say and improving based on it.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Putting the customer at the heart of every decision.
8 Proven Customer Strategy Examples
- Personalize Every Customer Interaction
- Engage Customers Across All Channels
- Develop a Loyalty Program with Clear Benefits
- Provide Proactive Support to Meet Customer Needs
- Gather and Act on Customer Feedback
- Build a Self-Service Hub
- Use Data to Drive Decisions
- Train Employees to Deliver Great Customer Service
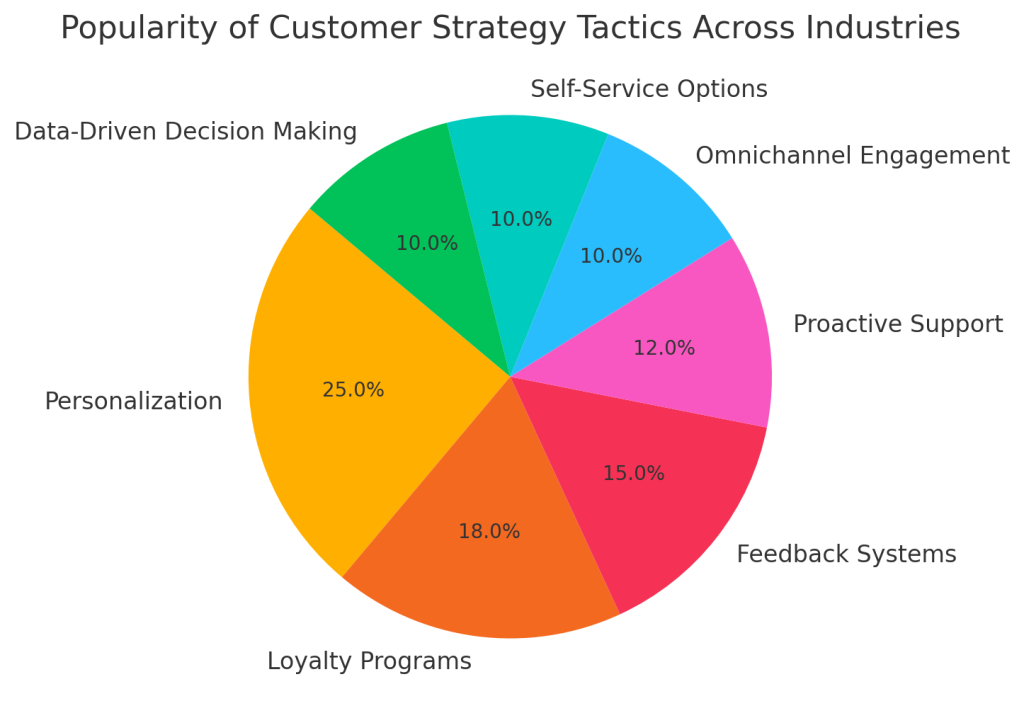
Here is a pie chart illustrating the popularity of different customer strategy tactics across various industries.
1. Personalize Every Customer Interaction
For businesses to effectively implement personalization, it’s essential to develop a systematic approach that integrates customer data with actionable insights.
Personalization goes beyond simply using a customer’s name – it requires creating a comprehensive customer onboarding process that captures and utilizes meaningful customer information at every touchpoint.
Successful personalization strategies require organizations to align their customer segmentation strategy across all departments.
Example: Netflix’s “Because you watched…” recommendations. They don’t just show you random shows; they analyze your viewing habits to suggest content you’ll actually enjoy.
How to Implement It:
- Start with basic customer segmentation:
- Age groups
- Shopping habits
- Purchase history
- Communication preferences
- Follow best customer onboarding practices:
- Welcome new customers personally
- Ask for preferences early
- Remember and use their preferences
- Check in after first purchase
- Use personalized customer experience touchpoints:
- Customized email greetings
- Birthday specials
- Purchase anniversary acknowledgments
- Tailored product recommendations
Quick Wins You Can Try Today:
- Start collecting customer names and birthdays
- Send personalized thank-you notes
- Remember customer preferences
- Follow up after purchases
2. Engage Customers Across All Channels
Customers today might connect with a brand on social media, visit their website, and chat with support—all in one day. So, to fully engage and acquire new customers, businesses need to adopt an omnichannel strategy.
Today’s customers expect consistency, and they want the flexibility to interact with a brand on their preferred platform without losing continuity.
For instance, if a customer starts a conversation with a chatbot on your website, then follows up in-store, they should feel as if they’re picking up right where they left off.
Example: Starbucks is a leader in omnichannel engagement. Customers can order and pay via the Starbucks app, track loyalty points, and pick up their drink in-store—all while enjoying a consistent experience across channels.
- Identify and Integrate Key Customer Channels:
- Website
- Mobile app
- Social media
- In-store
- Phone support
- Ensure each channel is optimized for ease of use.
- Unify Customer Data Across Platforms:
- Use a CRM system to gather and centralize data from all touchpoints.
- Make sure customer data is accessible across departments for a seamless experience.
- Map and Optimize the Customer Journey:
- Identify common paths (e.g., online browsing followed by in-store purchase).
- Design each touchpoint to complement others, creating a smooth transition between channels.
- Keep Messaging Consistent Across Channels:
- Align offers, branding, and messaging across all platforms.
- Use customer segmentation for personalized messages based on customer behavior.
Quick Wins You Can Try Today:
- Set up live chat on your website and link it to other support options.
- Ensure loyalty points or rewards are accessible across all platforms.
- Review responses to FAQs and make them consistent across channels.
3. Develop a Loyalty Program with Clear Benefits
A well-designed loyalty program encourages repeat business by rewarding customers for their actions like purchases, referrals, product reviews, and more.
Example: Sephora’s Beauty Insider program gives customers points for every purchase, redeemable for exclusive products, early access to sales, tiered reward system, and birthday gifts.
How to Implement It:
- Define clear rewards and tiers:
- Establish a simple point system (e.g., earn 1 point per dollar spent)
- Create tiers with increasing benefits (e.g., Bronze, Silver, Gold)
- Offer rewards that matter to your customers (discounts, freebies, exclusive access)
- Make enrollment easy:
- Allow customers to sign up online, in-store, or through an app
- Keep the registration process quick and straightforward
- Communicate the benefits:
- Highlight the rewards and how to earn them on your website and marketing materials
- Send regular updates on point balances and upcoming rewards
- Personalize the experience:
- Use customer data to offer tailored rewards
- Send personalized rewards on birthdays or anniversaries
Quick Wins You Can Try Today:
- Launch a basic loyalty program with immediate rewards
- Create a referral program
- Promote the program through all customer touchpoints
- Offer a sign-up rewards to encourage enrollment
4. Provide Proactive Support to Meet Customer Needs
Proactive support means anticipating customer issues and addressing them before they become problems. By reaching out first, you show customers that you value their experience and are committed to their satisfaction.
This approach reduces the number of incoming support requests and strengthens customer relationships.
Example: Spotify’s Service Notifications. Spotify notifies users in advance about upcoming changes, new features, or potential service interruptions. This keeps users informed and reduces confusion or frustration that might arise from unexpected changes
How to Implement It:
- Monitor customer interactions:
- Use analytics to identify common issues or questions.
- Track user behavior to anticipate needs.
- Communicate proactively:
- Send alerts about system updates or maintenance.
- Notify customers of delays or issues with their orders or services.
- Provide helpful resources:
- Offer tips or tutorials based on user activity.
- Share best practices to help customers get the most out of your product.
- Reach out after key events:
- Follow up after a purchase or sign-up to offer assistance.
- Check in if user activity drops to re-engage them.
Quick Wins You Can Try Today:
- Send a welcome email with helpful links after a new sign-up.
- Create automated messages for common issues before customers report them.
- Develop a knowledge base or FAQ section addressing frequent questions.
- Monitor social media mentions and address concerns before they’re escalated.
5. Gather and Act on Customer Feedback
Collecting customer feedback is crucial for understanding their needs, preferences, and areas where your business can improve. By actively seeking input and making changes based on that feedback, you show customers that you value their opinions, which can manage loyalty and satisfaction.
Example: Dropbox’s User Feedback Implementation. Dropbox regularly solicits feedback from its users to enhance its services. They have a “Tell us what you think” feature within the app, and they often implement popular suggestions in future updates, demonstrating that they listen and act on customer input.
How to Implement It:
- Solicit Feedback Through Multiple Channels:
- Send follow-up emails after purchases asking for reviews or suggestions.
- Incorporate feedback forms or chatbots on your website or app.
- Use social media polls or ask questions to engage customers.
- Make Providing Feedback Easy and Convenient:
- Keep surveys short and focused on key areas.
- Offer incentives like discounts or freebies for completing surveys.
- Ensure feedback mechanisms are mobile-friendly.
- Analyze and Act on Feedback:
- Regularly review feedback to identify common themes.
- Prioritize actionable items that can significantly improve customer experience.
- Implement changes and inform customers about updates made based on their feedback.
- Close the Feedback Loop:
- Thank customers for their input.
- Share success stories or improvements that resulted from customer suggestions.
- Encourage ongoing dialogue to keep the feedback channel open.
Quick Wins You Can Try Today:
- Include a simple feedback question in your email signature or newsletters.Customer feedback can also reveal high-demand products with low competition, along with niches, or business directions that weren’t obvious before.
- Add a “How did we do?” survey link after customer service interactions.
- Use tools like Google Forms or SurveyMonkey for quick setup.
- Keep an eye on reviews on platforms like Google, Yelp, or social media.
6. Build a Self-Service Hub
A self-service hub allows customers to find answers and solutions on their own, without needing to contact support. This feature is essential for today’s customers, who often prefer quick, independent help.
By providing resources like FAQs, troubleshooting guides, and how-to videos, a self-service hub empowers customers and improves their experience.
Example: Apple’s support hub includes FAQs, product manuals, and troubleshooting guides, allowing customers to resolve issues quickly without needing to speak to a representative.
How to Implement It:
- Create a Knowledge Base:
- Include FAQs, product manuals, and troubleshooting guides
- Organize topics by common issues or product categories
- Offer Step-by-Step Guides:
- Provide clear, simple instructions for common tasks (e.g., returns, account setup)
- Use visuals or videos to make complex steps easier to follow
- Keep Content Updated:
- Regularly review and update information based on customer feedback
- Add new FAQs or guides as new issues or products arise
Quick Wins You Can Try Today:
- Start by adding an FAQ section to your website
- Create simple how-to guides for common customer questions
- Add a search bar to help customers find relevant articles
- Use analytics to track which articles are most helpful
7. Use Data to Drive Decisions
Data is a powerful tool for understanding customer behavior and preferences. By analyzing customer data, businesses can make informed decisions that improve customer satisfaction and personalize the experience.
Data-driven customer strategy allows brands to predict needs, optimize offerings, and enhance customer engagement.
Example: Amazon uses data from customers’ past purchases, browsing history, and wish lists to recommend products that are relevant to each individual shopper.
How to Implement It:
- Collect Relevant Customer Data:
- Track purchase history, browsing behavior, and feedback
- Use analytics tools to gather insights on customer preferences
- Analyze and Segment Data:
- Group customers by behavior or demographics (e.g., frequent buyers, age groups)
- Identify trends and patterns to tailor your strategy
- Apply Insights to Improve Experiences:
- Personalize product recommendations
- Target promotions based on past purchases
- Adjust offerings based on popular demand
Quick Wins You Can Try Today:
- Review sales data to identify top-selling products
- Send targeted offers to high-value customer segments
- Use data to personalize email recommendations
8. Train Employees to Deliver Great Customer Service
Employees are often the face of your brand, and their interactions with customers can make a lasting impression. Investing in employee training ensures that your team is well-prepared to handle customer inquiries, solve problems effectively, and create positive experiences. When employees are equipped with the right skills, customers feel valued and are more likely to remain loyal.
Example: The Ritz-Carlton empowers its employees to go above and beyond, allowing them to spend up to $2,000 to resolve guest issues without needing manager approval.
How to Implement It:
- Provide Comprehensive Training:
- Cover essential skills such as active listening, problem-solving, and empathy
- Use role-playing to prepare employees for real-life customer interactions
- Encourage Empowerment and Flexibility:
- Allow employees to make small decisions to improve the customer experience
- Set guidelines but give them room to personalize interactions
- Focus on Ongoing Development:
- Offer regular training sessions to keep skills sharp
- Collect feedback from customers to identify training needs
Quick Wins You Can Try Today:
- Host a quick workshop on handling common customer questions
- Encourage employees to personalize greetings with customers’ names
- Empower employees to offer small gestures (e.g., discounts for long wait times)
- Gather feedback on customer service interactions to refine training
How Customer Strategy Varies by Industry
Now let’s look at how customer strategies can differ depending on the type of industry—B2C, B2B, and e-commerce.
1. B2C (Business-to-Consumer)
In B2C, the business is selling directly to everyday people. Examples include clothing brands or a tech gadget store. These customers are looking for fast, engaging, and often personalized interactions.
B2C companies focus on:
- Quick, Friendly Service: Customers expect simple, fast service.
- Personalized Offers: Small touches like personalized discounts or recommendations make customers feel seen.
- Loyalty Programs: Rewarding customers with points or perks encourages them to keep coming back.
Because B2C customers often make decisions quickly, the goal here is to build a connection fast and keep it strong.
2. B2B (Business-to-Business)
In B2B, the customers are other businesses. Examples: software companies that sell to corporations, or logistics services for large firms. These clients don’t make quick purchases; they need detailed information, reliability, and a solid return on investment.
B2B companies focus on:
- In-Depth Information: Providing case studies, white papers, and data to show the product’s value.
- Long-Term Relationships: Building trust over time through consistent, reliable service.
- Customer Education: Training, webinars, and support help clients understand and maximize the product’s benefits.
For B2B, the strategy is about showing value and forming a partnership that grows over the long term.
3. E-Commerce
For e-commerce, the entire experience happens online. Customers might never meet a sales rep or visit a physical store, so their impression comes only from the website or app.
E-commerce companies focus on:
- User-Friendly Websites: Smooth navigation and fast loading times are crucial.
- Personalized Recommendations: Using data to suggest relevant products makes shopping easier.
- Efficient Support Options: Offering live chat or a detailed FAQ ensures customers get answers fast.
E-commerce strategies are all about creating a smooth, enjoyable experience that keeps customers coming back.
Final Words
Acquiring and retaining customers isn’t complicated. It’s about building trust, being there when they need you, and showing you value their business. A good customer strategy does just that—simple, consistent actions that make customers feel appreciated.
Remember, your customers have choices. They can choose to walk away or they can choose to stay and become advocates for your brand. The difference lies in how you make them feel.
So, take these strategies to heart. Implement them not because they’re trendy, but because they represent a better way to do business—a human way.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ritz-Carlton is the best example of customer service strategy. Their “2,000 Rule” allows any employee to spend up to $2,000 per guest to solve an issue without managerial approval, empowering immediate problem resolution and exceptional service delivery.
HubSpot’s lifecycle-based contact strategy is the great example for customer contact strategy. It segments customers into awareness, consideration, and decision stages, delivering targeted content and support at each phase.
Amazon’s customer-obsessed strategy prioritizes long-term customer value over short-term profits, exemplified by their “Day 1” philosophy. This includes free returns, Prime benefits, and customer-driven product development.
Costco’s membership model delivers value through bulk pricing and high-quality products at low margin, focusing on customer savings over profit maximization.
Zappos’ customer-based structure eliminates traditional hierarchies, enabling all employees to prioritize customer needs. Their “Customer Loyalty Team” has no call time limits and is empowered to make decisions.